1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
|
# Import the opensees package for finite element analysis
import opensees.openseespy as ops
# Import some additional dependencies
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
plt.rcParams.update({'font.size': 16})
def make_model():
# Define a basic model with 2 dimensions and 3 degrees of freedom per node
# (translation in X and Y directions, and rotation about the Z-axis)
model = ops.Model(ndm=2, ndf=3)
#
# Define material
#
# Sets up an elastic material with given Young's modulus (E),
# moment of inertia (I), and cross-sectional area (A)
E = 200e6 # Young's modulus in kPa
I = 0.0001 # Area moment of inertia in m^4
A = 0.01 # Cross-sectional area in m^2
model.uniaxialMaterial("Elastic", 1, E)
#
# Create nodes
#
# Nodes are created along a vertical line with a defined height between each,
# representing floors of a building
numFloors = 56 # Number of floors
floorHeight = 3.0 # Height of each floor in meters
for i in range(numFloors + 1):
model.node(i + 1, 0, i * floorHeight)
# Fix base node
# The base node is fixed, meaning no translations or rotations are allowed,
# mimicking a fixed foundation
model.fix(1, 1, 1, 1)
# Define geometric transformation (required for beam-column elements)
## A linear geometric transformation is defined for beam-column elements,
## essential for how elements behave in the model space
model.geomTransf('Linear', 1)
# Define elements (cantilever columns)
# Beam-column elements are defined between each pair of nodes,
# simulating the columns of a building
for i in range(numFloors):
nodes = (i + 1, i + 2)
model.element("ElasticBeamColumn", i + 1, nodes, A, E, I, 1)
# Define mass
# Mass is assigned to each node (excluding the fixed base),
# essential for dynamic analysis like modal analysis
m = 2000 # Mass in kg
for i in range(1, numFloors + 1):
model.mass(i + 1, m, 1e-9, 0.0) # Mass assigned to each node
return model, numFloors, floorHeight
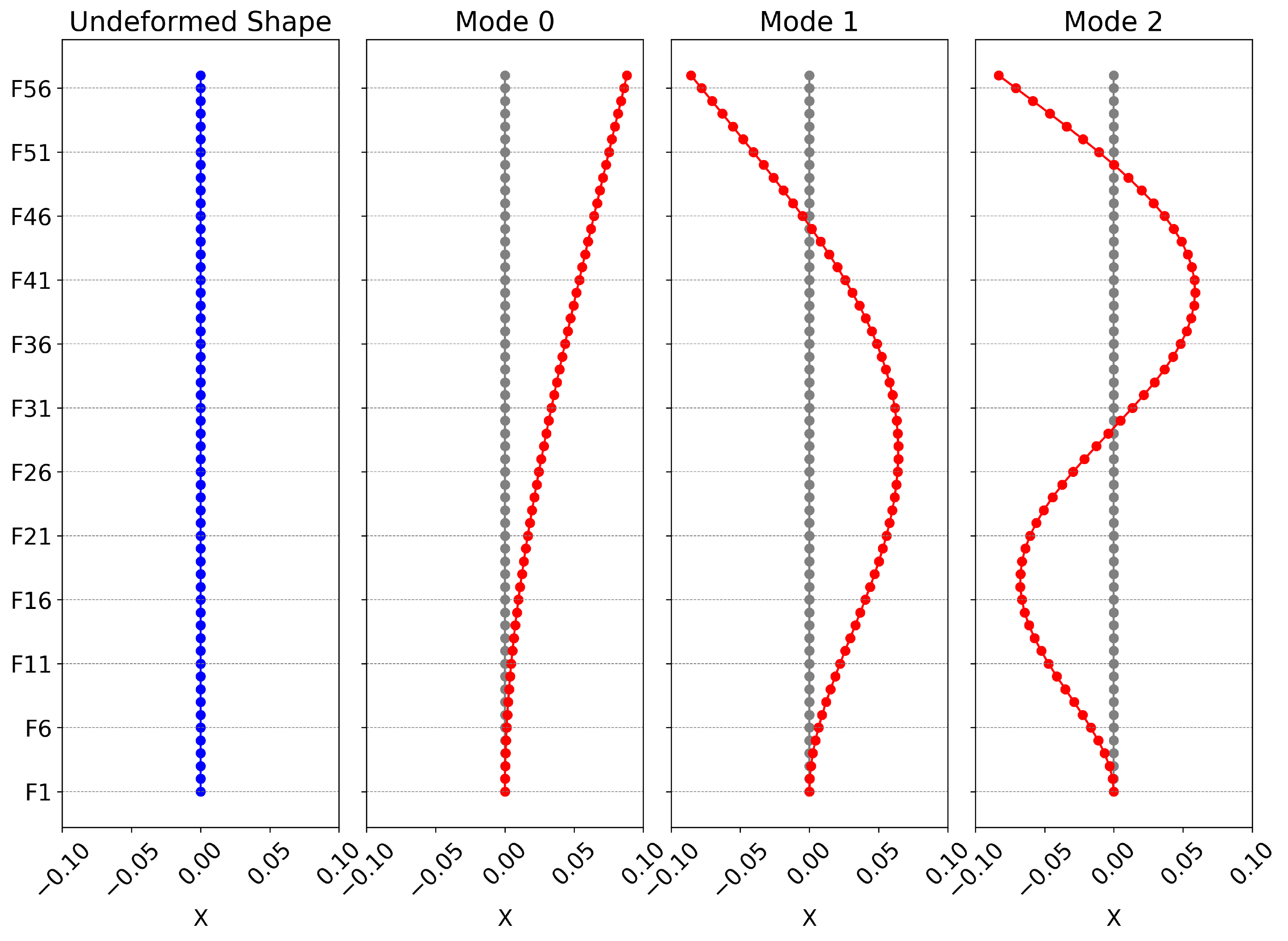
def plot_modes(model, numFloors, floorHeight):
# Perform eigenvalue analysis
# Eigenvalue analysis is performed to obtain the
# first three natural frequencies and associated mode shapes
numEigen = 3
eigenValues = model.eigen(numEigen)
# Plotting
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, numEigen + 1, figsize=(15, 10), sharey=True, gridspec_kw={'wspace': 0.1})
# Floor height positions and labels for y-ticks
floor_positions = [(i * floorHeight) for i in range(0, numFloors, 5)] # Every 5 floors
floor_labels = [f'F{i}' for i in range(1, numFloors + 1, 5)] # Every 5 floors
for fp, fl in zip(floor_positions, floor_labels):
print(f'Floor Position: {fp} - Floor Label: {fl}')
# Plot undeformed shape
for i in range(numFloors):
nodeTag_i = i + 1
nodeTag_j = i + 2
coord_i = model.nodeCoord(nodeTag_i) # Get the coordinates of the i-th node
coord_j = model.nodeCoord(nodeTag_j) # Get the coordinates of the j-th node
ax[0].plot([coord_i[0], coord_j[0]], [coord_i[1], coord_j[1]], 'b-o')
ax[0].set_title('Undeformed Shape')
ax[0].set_xlabel('X')
# ax[0].set_ylabel('Y')
ax[0].set_yticks(floor_positions)
ax[0].set_yticklabels(floor_labels) # Adjust fontsize as needed
# Plot mode shapes
all_modal_displacements = {}
for mode in range(numEigen):
for i in range(numFloors):
nodeTag_i = i + 1
nodeTag_j = i + 2
coord_i = model.nodeCoord(nodeTag_i) # Get the coordinates of the i-th node
coord_j = model.nodeCoord(nodeTag_j) # Get the coordinates of the j-th node
ax[mode + 1].plot([coord_i[0], coord_j[0]], [coord_i[1], coord_j[1]], '-o', color='gray')
# get modal displacement and floor number for each node
all_modal_displacements[mode] = {}
# Scale deformation to the node coordinates for easy visualization
scaleFactor = 15 # Scale factor for deformation amplification
for i in range(numFloors):
nodeTag_i = i + 1
nodeTag_j = i + 2
coord_i = model.nodeCoord(nodeTag_i)
coord_j = model.nodeCoord(nodeTag_j)
eigenvector_i = model.nodeEigenvector(nodeTag_i, mode + 1)
eigenvector_j = model.nodeEigenvector(nodeTag_j, mode + 1)
# Apply scale factor to mode shape
coord_i[0] += scaleFactor * eigenvector_i[0]
coord_j[0] += scaleFactor * eigenvector_j[0]
all_modal_displacements[mode][nodeTag_i] = coord_i[0]
ax[mode + 1].plot([coord_i[0], coord_j[0]], [coord_i[1], coord_j[1]], 'r-o')
print(f'Mode {mode + 1} - Frequency: {np.sqrt(eigenValues[mode]) / (2 * np.pi)} Hz')
# print(f'Modal Displacements: {modalDisplacements}')
ax[mode + 1].set_title(f'Mode {mode}')
ax[mode + 1].set_xlabel('X')
ax[mode + 1].set_ylim(ax[0].get_ylim())
# ax[mode + 1].set_yticks(floor_positions)
# ax[mode + 1].set_yticklabels(floor_labels)
## Draw horizontal line at each floor level
for a in ax:
for y in floor_positions:
a.axhline(y, color='gray', linestyle='--', linewidth=0.5)
## rotate x-axis labels
for a in ax:
plt.sca(a)
plt.xticks(rotation=45)
max_disp = 0.1
for a in ax:
a.set_xlim([-max_disp, max_disp])
plt.savefig('mode_shapes.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
# print(all_modal_displacements)
## all_modal_displacements to pandas dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame(all_modal_displacements)
# print(df.head())
## ylocations for each mode
yloc_offset = 0.1
ylocations = [i * yloc_offset for i in range(df.shape[1])]
print(ylocations)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(12, 8))
# plot for first mode
ax.plot(df[0], 'bo-', label='Mode 1')
ax.axhline(ylocations[0], color='black', linestyle='--', linewidth=1.0)
## plot for second mode with yaxis offset of 0.5
ax.plot(df[1] + ylocations[1], 'ro-', label='Mode 2')
ax.axhline(ylocations[1], color='black', linestyle='--', linewidth=1.0)
## plot for third mode with yaxis offset of 1.0
ax.plot(df[2] + ylocations[2], 'go-', label='Mode 3')
ax.axhline(ylocations[2], color='black', linestyle='--', linewidth=1.0)
ax.set_xlabel('Floor Number')
ax.set_ylabel('Normalized Displacement')
## xticks
ax.set_xticks(range(1, numFloors + 1, 5))
## yticks for each mode
ax.set_yticks(ylocations)
ax.set_yticklabels([f'Mode {i}' for i in range(len(ylocations))])
plt.savefig('modal_displacements.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
if __name__ == '__main__':
plot_modes(*make_model())
|