For the case of the uniaxial section, moment-curvature and axial force-deformation curves are defined independently, and numerically.
For the case of the fiber sections (steel and RC), uniaxial materials are defined numerically (stress-strain relationship) and are combined into a fiber section where moment-curvature and axial force-deformation characteristics and their interaction are calculated computationally.
Uniaxial Section |
Notes
|
AISC Standard W Section |
Notes
|
Reinforced Concrete Section -- Rectangular Symmetric Section, Unconfined Concrete |
Notes
|
Reinforced Concrete Section -- Rectangular Symmetric Section, Confined Concrete Core |
Notes
|
Reinforced Concrete Section -- Rectangular Section |
Notes
|
Reinforced Concrete Section -- Circular Section, Confined Core |
Notes
|
Reinforced Concrete Hollow Section -- Symmetric Section, Confined Concrete |
Notes
|
Moment-Curvature Analysis
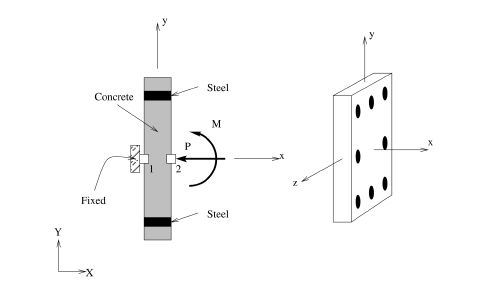
- This example introduces the moment-curvature procedures for sections in 2D or 3D space, as built in the previous section. (the only difference between them is the degree-of-freedom corresponding to curvature).
- The moment-curvature analysis of a section is by creating a zero-length rotational-spring element. This section is subjected to a user-defined constant axial load and to a linearly-increasing moment to a user-defined maximum curvature.
2D Moment-Curvature Analysis |
Files | Notes |
3D Moment-Curvature Analysis |
Files |
Run
The model and analysis combinations for this example are numerous. The following are an small subset, for demonstration purposes:
- To run Uniaxial-Section Model, 2D
puts " --------------------------------- 2D Model ---------------" puts " a. Uniaxial Section" source Ex9a.build.UniaxialSection2D.tcl source Ex9.analyze.MomentCurvature2D.tcl
- To run RC Section: Rectangular, Confined, Symmetric Model, 3D
puts " --------------------------------- 3D Model ---------------" puts " d. RC Section: Rectangular, Confined, Symmetric" source Ex9d.build.RectConfinedSymm3D.tcl source Ex9.analyze.MomentCurvature3D.tcl